Atmospheric Thermoelectric Module Evaluation System
F-PEM

The system can evaluate the power generation and heat flow that can be gathered when the temperature difference is given to thermoelectric module in the environment(in atmosphere and under load) and conversion efficiency that can be calculated from maximum power generation and heat flow. In addition, this system can conduct long-hours operation and heat cycle tests of thermoelectric modules and can be used for testing newly developed modules as well as for durability tests under load and temerature in which commercially available modules are actually incorporated.
Applications
- Evaluation of maximum power generation and heat flow of thermoelectric modules in air and under load
- Evaluation of conversion efficiency of module calculated from maximum power generation and heat flow
- Evaluation of durability of thermoelectric modules by long-hours measurement
Features
- The output of characteristics of the module can be evaluated by continuous loading at a high temperature in air.
- Repeated measurement of Pmax is possible at constant intervals while continuing to apply load for a long time.
- Measurement can be performed while applying a constant load in accordance with the actual module built-in environment.
Specifications
| Measurement properties | Power generation, Heat flow, Conversion efficiency |
|---|---|
| Temperature range | Room temperature to 600℃ (heater setting value) |
| Sample size | 40mm-square (Standard) |
| Measurement atmosphere | In air |
Utility
| Outside dimensions | W600 x D600 x H1700 (mm) |
|---|---|
| Weight | Approx. 120kg |
| Power | Single phase AC200V, 5kW (main body) Single phase AC100V, 1kW (PC) |
Sample system chart
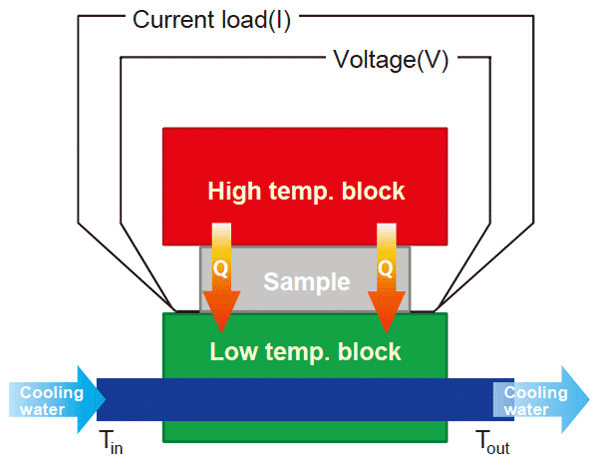
- I
- Current load
- V
- Voltage
- C
- Heat capacity of water
- v
- Flow rate of water
- Tout
- Outlet temp. of water
- Tin
- Inlet temp. of water
Power generation(P) = IV
Heat flow(Q) = Cv (Tout- Tin)
Conversio efficiency(η)=P / (P + Q)
Measurement example of oxide TEG
Pmax
Heat flow
Efficiency max
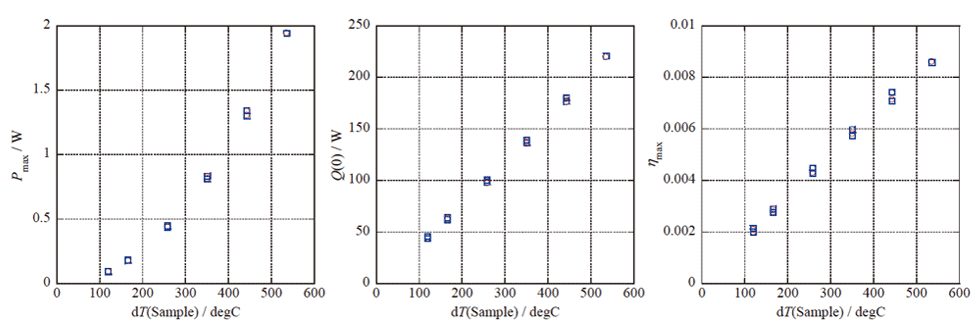
Pma
Heat flow
Efficiency max
論文リスト
Development and Verification of Evaluation Instrument of Thermoelectric Module in Air
The Journal of the Thermoelectrics Society of Japan Vol. 15, No. 2 (2018), pp. 85-88
©2018 The Thermoelectrics Society of Japan
Analysis service by using this product
Related product

Infrared lamp heating system RTP-mini

Thermal Flow Rate Evaluation System for Low Thermal Resistance Multilayer Substrates F-CAL

Ultra High Precision Thermal Expansion Measurement System by Laser Interferometer SuperLIX

Polymeric Thermoelectric Sheet Evaluation System ZEM-d

Seebeck Coefficient / Electric Resistance Measurement System ZEM-3 series

Atmospheric Thermoelectric Module Evaluation System F-PEM
Atmospheric Thermoelectric Module Evaluation System F-PEM Contact form
The information that you enter will only be used to provide you with a response. However, when you request that we mail you a catalog or other materials, please understand that the shipper specified by ADVANCE RIKO may use only the information necessary to send those materials, such as your name and address.
Please check our privacy policy for more details.