Arc-Plasma method nano-particle Deposition System
APD series

New nanoparticle deposition system using pulse vacuum arc discharge
Pulse vacuum arc deposition is a unique technique to deposit ultrathin films and nanoparticles by generating metal ions in a simple process. This system can achieve high in terms of film flatness and particle fineness, which is impossible with other systems.
Applications
- APD-S (Substrate deposition model)
Metal film (magnetism, Plasmon, protection film) - APD-P (Powder support model)
Fuel cell catalyst by use of nanoparticles, exhaust gas catalyst, photocatalyst, VOC dispersed catalyst, carbon nanotube catalyst, Plasmon
Features
- Capable of selecting freely nanoparticle diameter from approx.1.5nm to 6 nm by changing condenser capacity
- Any conductive materials (targets) can be converted into plasma.
*Specific resistance of a target: 0.01Ωcm or less - Nanoparticles supported by this system show highly active catalytic effect compared with ones produced through wet process.
Specifications
| Model | APD-S | APD-P |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | Substrate φ 2 inch |
Powder Vessel size (inside dimension) φ 95 × H 30 (mm) with stirring mechanism |
| Standard deposition numbers | 1 | 1 |
Mechanism
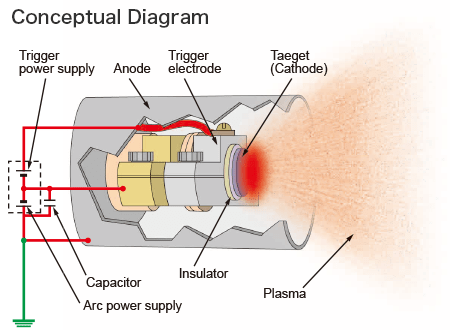
Five Futures
- The system can select nano-particle diameter within the range of approx. 1.5nm to 6nm by changing condenser capacity.
- The system can make any material plasmatic in case they are electrically-conductive materials(target).
*Specific resistance for target is 0.01 ohm cm or less - The system can readily generate oxide and nitride by changing atmosphere.
Also, when graphite is discharged in H2 gas, it generates UNCD(Ultrananocrystalline diamond). - The nano-particles supported by the system shows active catalytic effects as compared with wet process.
- Model APD-P supports nano-particles to powders.
Model APD-S supports nano-particles to 2-inch substrate.
*The above-mentioned 1, 3 and 4 depend on literatures.
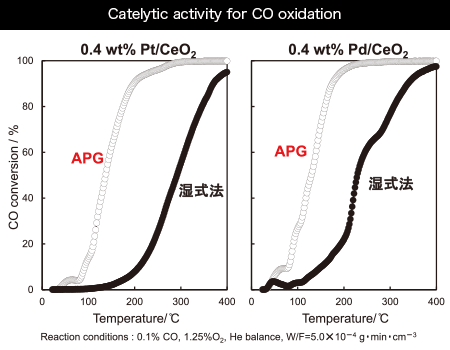
Quoted literatures: “Ministry of Education, element strategic project achievement” by Professor Machida at Kumamoto University
Relation between condenser capacity and nano-particle size
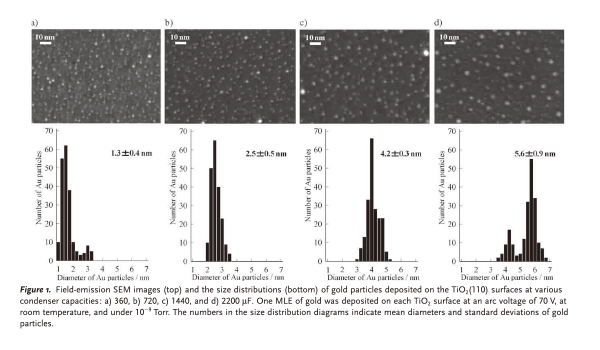
Chemistry in National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
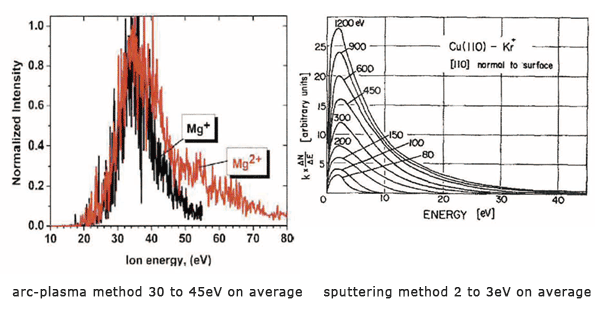
The difference in energies largely contributes to the generation and function of nano-particles.
(The vertical axis is no unit of quantity required due to relative values.)
Quoted literatures: Arc-plasma J. Appl. Phys. 101(2007)043304 SputterJ. Appl. Phys. 35(1964)1819
Publication List
- C-dopand
MBE growth mode and C incorporation of GeC epilayers on Si (001) substrates using arc plasma gun as a novel C cource
Motoki Okinaka*, Yasumasa Hamana1, Takashi Tokuda, Jun Ohta, Masahiro Nunoshita
Journal of Crystal Growth 249 (2003) 78-86 - Characterisation of NPs by APD
Ultra-small platinum and gold nanoparticles by arc plasma deposition
Sang Hoon Kima,∗, Young Eun Jeonga, Heonphil Haa, Ji Young Byuna, Young Dok Kimb
Applied Surface Science 297 (2014) 52–58
10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.072 - HRTEM analyses of the platinum nanoparticles prepared on graphite particles using coaxial arc plasma deposition
Kun'ichi Miyazawa, Masaru Yoshitake, Yumi Tanaka
J Nanopart Res (2017) 19:191
10.1007/s11051-017-3895-6 - Characterisation of NPs by APD in ionic liquids
Temperature-independent formation of Au nanoparticles in ionic liquids by arc plasma deposition
Yoshikiyo Hatakeyama a,1, Satoshi Kimura b, Tatsuya Kameyama c, Yoshiaki Agawa d, Hiroyuki Tanaka d, Ken Judai a, Tsukasa Torimoto c, Keiko Nishikawa b,⇑
Chemical Physics Letters 658 (2016) 188–191
10.1016/j.cplett.2016.06.044 - CNT catalyst
High-density horizontally aligned growth of CNT with Conanoparticles deposited by Arc discharge plasma method
D. Phokharatkul,1 Y. Ohno,1,a H. Nakano,2 S. Kishimoto,1 and T. Mizutani1
APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 93, 053112 2008
10.1063/1.2969290 - Robust Noise Modulation of Nonlinearity in Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistors
Toshio Kawahara , Satarou Yamaguchi, Kenzo Maehashi1, Yasuhide Ohno1, Kazuhiko Matsumoto1, and Tomoji Kawai1
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 49 (2010) 02BD11
10.1143/JJAP.49.02BD11 - High-Rate Growth of Films of Dense, Aligned Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Using Microwave Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Mineo HIRAMATSU, Hidetoshi NAGAO1, Masaki TANIGUCHI1, Hiroshi AMANO1, Yoshinori ANDO1 and Masaru HORI2
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 22, 2005, pp. L 693–L 695
10.1143/JJAP.44.L693 - Combinatorial
Combinatorial Arc Plasma Deposition of Thin Films
Seiichi HATA , Ryusuke YAMAUCHI1, Junpei SAKURAI1 and Akira SHIMOKOHBE1
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 45, No. 4A, 2006, pp. 2708–2713
10.1143/JJAP.45.2708 - Combinatorial Search for Low Resistivity Pd–Cu–Si Thin Film Metallic Glass Compositions
Ryusuke YAMAUCHI , Seiichi HATA1, Junpei SAKURAI and Akira SHIMOKOHBE
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 45, No. 7, 2006, pp. 5911–5919
10.1143/JJAP.45.5911 - Searching for Novel Ru-Based Thin Film Metallic Glass by Combinatorial Arc Plasma Deposition
Junpei SAKURAI , Seiichi HATA1, Ryusuke YAMAUCHI, and Akira SHIMOKOHBE
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 46, No. 4A, 2007, pp. 1590–1595
10.1143/JJAP.46.1590 - Dye sensitizing
Transparent conductive oxide layer-less dye-sensitized solar cells consisting of floating electrode with gradient TiOx blocking layer"
Yoshikazu Yoshida,1 Shyam S. Pandey,1 Kenshiro Uzaki,1 Shuzi Hayase,1,a Mitsuru Kono,2 and Yoshihiro Yamaguchi2
APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 94, 093301 2009
10.1063/1.3089845 - Exhaust gas catalyst
CO oxidation activity of thermally stable Fe–Cu/ CeO2 catalysts prepared by dual-mode arc-plasma process
Satoshi Hinokuma,abc Noriko Yamashita,a Yasuo Katsuhara,a Hayato Kogamia and Masato Machida*ab
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015, 5, 3945
10.1039/c5cy00370a - Nanoparticle catalyst preparation using pulsed arc plasma deposition
Satoshi Hinokuma,abc Satoshi Misumi,a Hiroshi Yoshidab and Masato Machida*ab
Cite this: Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015, 5, 4249
10.1039/c5cy00636h - Effect of thermal ageing on the structure and catalytic activity of Pd/CeO2 prepared using arc-plasma process
Satoshi Hinokuma,ab Hiroaki Fujii,a Yasuo Katsuhara,a Keita Ikeueab and Masato Machida*ab
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014, 4, 2990
10.1039/c4cy00291a - Pd Fe/CeO2 bimetal catalysts prepared by dual arc-plasma deposition
Satoshi Hinokuma1, Yasuo Katsuhara, Eriko Ando, Keita Ikeue, Masato Machida∗
Catalysis Today 201 (2013) 92– 97
10.1016/j.cattod.2012.03.063 - Structure and catalytic property of supported rhodium catalysts prepared using arc-plasma
Satoshi Hinokumaa,b, MadokaOkamotob, ErikoAndob, KeitaIkeueb, MasatoMachidab,∗
Catalysis Today xxx (2011) xxx–xxx
10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.008 - A nanometric Rh overlayer on a metal foil surface as a highly efficient three-way catalyst
Satoshi Misumi1, Hiroshi Yoshida1,2, Satoshi Hinokuma1,2,3, Tetsuya Sato4 & Masato Machida1,2
10.1038/srep29737 - Subnano-particle Ce catalyst prepared by pulsed arc-plasma process
Satoshi Hinokuma a,b,c, Hayato Kogami a, Noriko Yamashita a, Yasuo Katsuhara a, Keita Ikeue a,b, Masato Machida a,b,*
Catalysis Communications 54 (2014) 81–85
10.1016/j.catcom.2014.05.025 - Arc Plasma Processing of Pt and Pd Catalysts Supported on c-Al2O3 Powders
S. Hinokuma Æ K. Murakami Æ K. Uemura Æ M. Matsuda Æ K. Ikeue Æ N. Tsukahara Æ M. Machida
Top Catal (2009) 52:2108–2111
10.1007/s11244-009-9387-x - Fuel cell
Pt−Ni Nanoparticle-Stacking Thin Film: Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Naoto Todoroki,* Takashi Kato, Takehiro Hayashi, Shuntaro Takahashi, and Toshimasa Wadayama
ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2209−2212
10.1021/acscatal.5b00065 - The d-Band Structure of Pt Nanoclusters Correlated with the Catalytic Activity for an Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Eishiro Toyoda,*,† Ryosuke Jinnouchi,† Tatsuya Hatanaka,† Yu Morimoto,† Kei Mitsuhara,‡ Anton Visikovskiy,‡ and Yoshiaki Kido‡
J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 21236–21240
10.1021/jp206360e - 2D Platinum Network ORR Catalyst on Carbon and Niobium Oxide Hybrid Support
C. Xu1, J. Yang1, B. L. Pence1, K. Gath1, P. Pietrasz1, M. Sulek1, K. Sun2, E. Sohm3, G. Meng3
ECS Transactions, 64 (3) 181-189 (2014)
10.1149/06403.0181ecst - Preparation of Pt/C Catalyst by Coaxial Arc Plasma Deposition for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
Yoshiaki Agawa,a,b,z Masayuki Kunimatsu,c Takeshi Ito,d Yasutaka Kuwahara,a and Hiromi Yamashitaa
ECS Electrochemistry Letters, 4 (10) F57-F60 (2015)
10.1149/2.0091510eel - Gold catalyst
Hydrogen Dissociation by Gold Clusters
Tadahiro Fujitani,* Isao Nakamura, Tomoki Akita, Mitsutaka Okumura, and Masatake Haruta
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9515 –9518
10.1002/anie.200905380 - Graphene layer growth catalyst
Graphene layer growth on silicon substrates with nickel film by pulse arc plasma deposition
K. Fujita,a) K. Banno, H. R. Aryal,b) and T. Egawa
APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 101, 163109 (2012)
10.1063/1.4761474 - Hydrogen peroxide solution
High performanceofhydrogenperoxidedetectionusingPt nanoparticles-dispersedcarbonelectrodepreparedbypulsedarc plasma deposition
Takeshi Ito a,n, MasayukiKunimatsu a, SatoruKaneko a, YasuoHirabayashi a, MasayasuSoga a, Yoshiaki Agawa b, KojiSuzuki c
Talanta 99(2012)865–870
10.1016/j.talanta.2012.07.048 - Magnetic thin film
Magnetic properties of Nd–Fe–B thick film magnets prepared by using arc deposition
M. Nakano, M. Sahara,a K. Yamawaki, T. Yanai, and H. Fukunaga
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 107, 09A744 2010
10.1063/1.3348233 - Nanocomposite Nd-Fe-B/α-Fe Thick-Film Magnets Prepared by Vacuum Arc Deposition
Masaki Nakano, Tomoaki Tsutsumi, Takeshi Yanai, and Hirotoshi Fukunaga
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2014 - Photo catalyst
Improved Inactivation Effect of Bacteria: Fabrication of Mesoporous Anatase Films with Fine Ag Nanoparticles Prepared by Coaxial Vacuum Arc Deposition
H. Oveisi, S. Rahighi, X. J., Y.i Agawa, A. Beitollahi, S. Wakatsuki, and Y. Yamauchi
10.1246/cl.2011.420 - Prox catalyst
Support Effect of Arc Plasma Deposited Pt Nanoparticles/TiO2 Substrate on Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation
Kamran Qadir,†,§ Sang Hoon Kim,‡,§ Sun Mi Kim,† Heonphil Ha,‡ and Jeong Young Park*,†
J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24054−24059
10.1021/jp306461v - Catalytic activity of Au TiO2 and Pt TiO2 nanocatalysts prepared with arc plasma deposition under CO oxidation
Sang Hoon Kima,1, Chan-Ho Jungb,c,1, Nruparaj Sahub,c, Dahee Parkb,c, Jung Yeul Yund, Heonphil Haa, Jeong Young Parkb,c,∗
Applied Catalysis A: General 454 (2013) 53– 58
10.1016/j.apcata.2012.12.049 - Thermoelectric element
Fabrication by Coaxial-Type Vacuum Arc Evaporation Method and Characterization of Bismuth Telluride Thin Films
M. UCHINO,1 K. KATO,2 H. HAGINO,1 and K. MIYAZAKI1,3
Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, 2013 TMS
10.1007/s11664-012-2438-2 - TiN film
Synthesis of TiN thin film on diamond surface for ferrous metal contacts by a new atom beam method
Hiroshi Kinoshitaa,∗, Shunsuke Yamamotob, Hideaki Yatanib, Tetsuo Nakaic, Nobuo Ohmaeb
Applied Surface Science 258 (2012) 3002– 3006
10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.11.026 - Ultrananocrystalline Diamond/Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbon Composite Films
Structural and Physical Characteristics of Ultrananocrystalline Diamond/Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbon Composite Films Deposited Using a Coaxial Arc Plasma Gun
T. Yoshitake, Y. Nakagawa, A. Nagano, R. O., H. Setoyama1, E. Kobayashi1, K. Sumitani1, Y. Agawa and K. Nagayama
Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49 (2010) 015503
Analysis service by using this product
Related product

Infrared lamp heating system RTP-mini

Thermal Flow Rate Evaluation System for Low Thermal Resistance Multilayer Substrates F-CAL

Ultra High Precision Thermal Expansion Measurement System by Laser Interferometer SuperLIX

Polymeric Thermoelectric Sheet Evaluation System ZEM-d

Seebeck Coefficient / Electric Resistance Measurement System ZEM-3 series

Atmospheric Thermoelectric Module Evaluation System F-PEM
Arc-Plasma method nano-particle Deposition System APD series Contact form
The information that you enter will only be used to provide you with a response. However, when you request that we mail you a catalog or other materials, please understand that the shipper specified by ADVANCE RIKO may use only the information necessary to send those materials, such as your name and address.
Please check our privacy policy for more details.